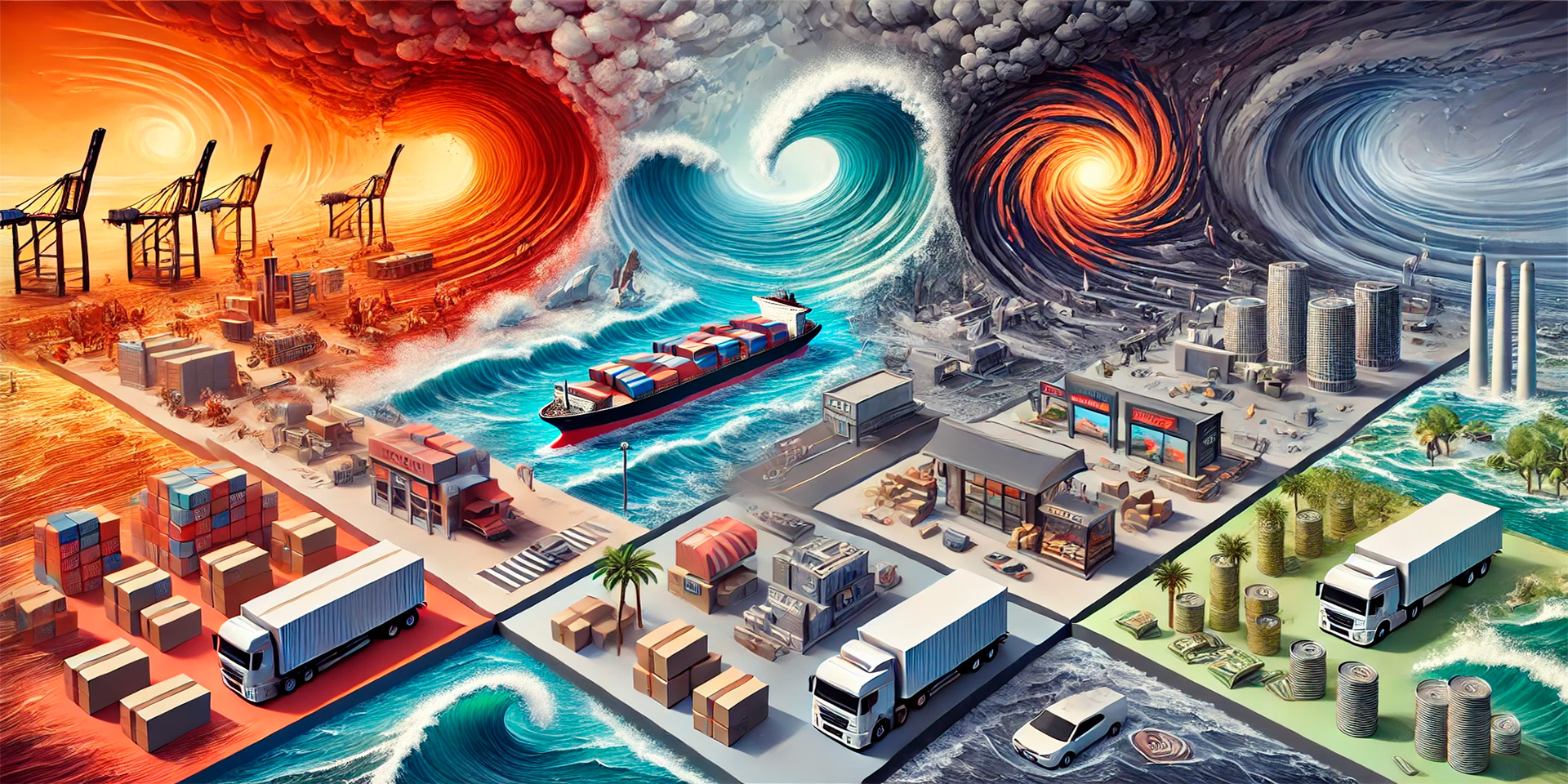
From Storms to Shortages: The Ripple Effect of Extreme Weather on Prices
Extreme weather events, from hurricanes and floods to droughts and wildfires, can have a profound impact on global supply chains. As these events become more frequent due to climate change, businesses and consumers alike are feeling the effects. Supply chains, which rely on predictable transport routes, labor, and infrastructure, are particularly vulnerable to weather disruptions. When weather conditions disrupt the movement of goods, it leads to delays, shortages, and, ultimately, higher prices for consumers.
This article examines how climate conditions affect supply chains and explores the ripple effects on consumer prices.
How Extreme Weather Disrupts Supply Chains
Supply chains are complex networks that involve the movement of goods from manufacturers to distributors, retailers, and, eventually, consumers. These processes depend on reliable infrastructure, transportation, and labor. When extreme weather events occur, they can cause significant disruptions in several key areas of the supply chain.
1. Damage to Infrastructure
Severe weather, such as hurricanes, floods, or earthquakes, can damage critical infrastructure, including roads, bridges, ports, and airports. When these transportation routes are compromised, goods cannot move efficiently from one point to another, causing delays and bottlenecks throughout the supply chain.
Impact on supply chains:
- Delayed shipments: Damaged roads and railways can lead to prolonged delays in the delivery of goods, particularly for industries that rely on just-in-time delivery systems.
- Increased transportation costs: Alternative routes, such as air transport or longer ground routes, may need to be used, increasing the overall cost of transporting goods.
2. Labor Shortages and Disruptions
Extreme weather conditions can also affect the availability of labor, especially in regions where the workforce is directly impacted by natural disasters. Workers may be unable to reach their places of employment due to dangerous conditions or may be displaced from their homes, resulting in labor shortages that hinder supply chain operations.
Consequences of labor disruptions:
- Reduced productivity: Manufacturing facilities and warehouses may see lower output when workers are unable to perform their duties, leading to delays in product availability.
- Increased labor costs: In some cases, companies may need to hire temporary workers or pay overtime to maintain production levels, driving up costs.
3. Interruptions in Raw Material Supply
Weather events can disrupt the supply of raw materials needed for manufacturing. For example, droughts may affect agricultural yields, while hurricanes or floods may damage mining operations or forests. When raw materials are scarce or delayed, production processes slow down, leading to product shortages and higher prices.
Examples of raw material disruptions:
- Agriculture: Droughts or floods can reduce crop yields, affecting food supply chains and leading to higher prices for products such as grains, fruits, and vegetables.
- Mining: Flooding or landslides in mining regions can reduce the availability of metals and minerals used in electronics, construction, and manufacturing, driving up costs.
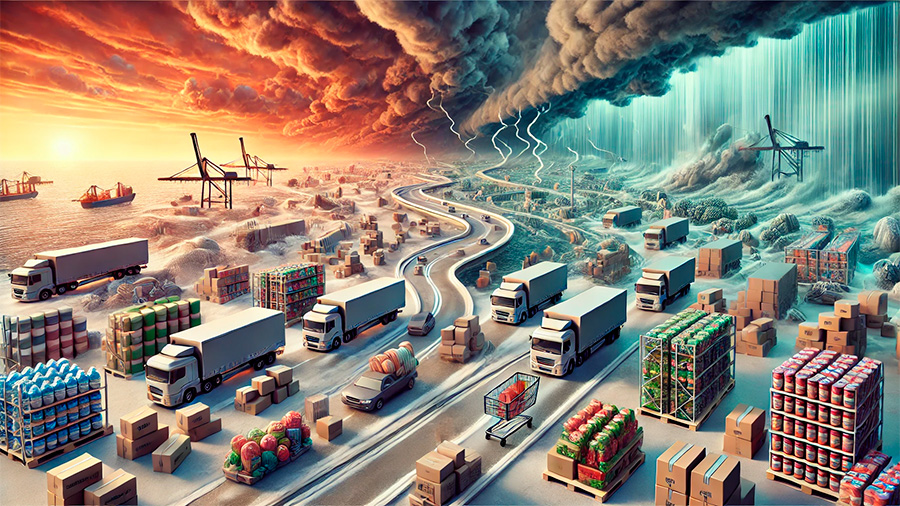

The Ripple Effect on Consumer Prices
When supply chains are disrupted by extreme weather, the costs associated with transportation, labor, and raw materials increase. These additional costs are typically passed on to consumers in the form of higher prices. The following factors contribute to price inflation during periods of supply chain disruption caused by weather events.
1. Increased Shipping Costs
As extreme weather events cause damage to infrastructure and create obstacles for transportation, shipping costs rise. Whether it’s rerouting shipments to avoid flooded areas or relying on more expensive air transport due to damaged roads, businesses face higher transportation costs, which are then reflected in the price of goods.
Impact on consumers:
- Higher retail prices: Retailers may increase prices on goods that are more expensive to transport due to weather-related disruptions.
- Scarcity pricing: In some cases, shortages caused by transportation delays may lead to price hikes for high-demand products.
2. Supply Shortages and Limited Availability
When extreme weather events disrupt the production or delivery of goods, supply shortages can occur. These shortages often lead to higher prices, especially for essential goods such as food, fuel, and medical supplies. With fewer products available, businesses may charge premium prices for limited inventory.
Examples of supply shortages:
- Fuel shortages: Hurricanes or severe storms can disrupt oil refineries and fuel distribution networks, leading to higher gasoline prices.
- Food price inflation: Agricultural disruptions caused by droughts or floods can reduce the supply of key food products, leading to price increases in grocery stores.
3. Increased Costs of Goods Production
When raw materials are difficult to obtain due to weather-related disruptions, manufacturers face increased costs to produce goods. These higher production costs, whether due to more expensive raw materials or higher labor costs, ultimately lead to higher prices for consumers. Industries such as construction, electronics, and agriculture are particularly vulnerable to raw material shortages caused by extreme weather.
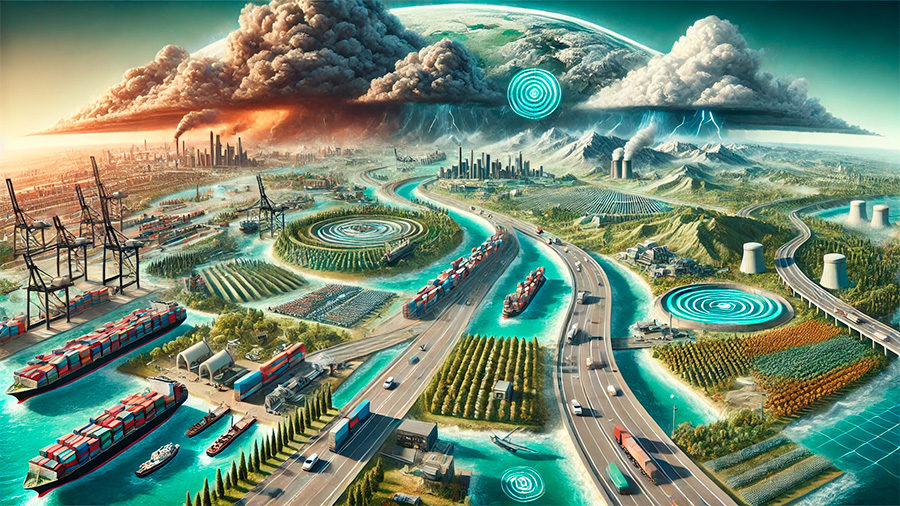

Climate Change and the Future of Supply Chains
As climate change continues to exacerbate the frequency and intensity of extreme weather events, the global supply chain will face increasing challenges. Businesses are beginning to recognize the importance of building resilience into their supply chains to minimize the impact of weather-related disruptions. However, adapting to these challenges requires long-term investments in infrastructure, technology, and alternative supply routes.
1. Diversification of Supply Chains
One of the ways businesses are addressing the growing threat of climate-related disruptions is by diversifying their supply chains. By sourcing raw materials and products from multiple locations or regions, companies can reduce their dependence on any one area that may be vulnerable to extreme weather.
Benefits of diversification:
- Reduced risk: Sourcing materials from diverse locations helps mitigate the impact of localized weather events, ensuring a steady supply of goods.
- Improved flexibility: Having multiple supply sources allows businesses to adapt quickly to weather disruptions, reducing delays and shortages.
2. Investment in Climate-Resilient Infrastructure
Governments and businesses are increasingly investing in climate-resilient infrastructure to protect supply chains from the effects of extreme weather. This includes improving roads, bridges, and ports to withstand storms and floods, as well as enhancing technology for real-time monitoring of weather patterns and supply chain performance.
Examples of climate-resilient investments:
- Reinforced infrastructure: Coastal cities are investing in flood defenses and strengthening ports to protect against rising sea levels and storm surges.
- Early warning systems: Advanced weather forecasting and early warning systems allow businesses to prepare for and respond to weather disruptions more effectively.
Conclusion
Extreme weather events caused by climate change are having an increasingly significant impact on global supply chains. Damage to infrastructure, labor disruptions, and interruptions in the supply of raw materials all contribute to higher costs and delays in the delivery of goods. These disruptions result in higher prices for consumers, especially for essential products such as food, fuel, and medical supplies.
To mitigate the effects of extreme weather on supply chains, businesses are investing in diversification and climate-resilient infrastructure. As climate change continues to shape the future of global supply chains, these strategies will become critical in maintaining the flow of goods and minimizing price inflation for consumers.
Calendar
| M | T | W | T | F | S | S |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | ||
| 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 |
| 13 | 14 | 15 | 16 | 17 | 18 | 19 |
| 20 | 21 | 22 | 23 | 24 | 25 | 26 |
| 27 | 28 | 29 | 30 | 31 | ||